cubital tunnel compression test|positive tinel's sign foot : mail order Cubital tunnel syndrome happens when that nerve is irritated or compressed. A compressed ulnar can cause various uncomfortable and severe symptoms that, if left . Resultado da With two children in foster care, Gia, a pregnant single mother pitted against the system, fights to reclaim her family. In her close-knit Bay Area .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web27 de mai. de 2023 · Confira as dezenas sorteadas, os ganhadores e o valor do prêmio da Dupla-Sena 2520, realizada em 27 de maio de 2023, com premiação estimada em .
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome is a compressive neuropathy of the ulnar nerve caused by anatomic compression in the medial elbow. Diagnosis is made clinically with presence of sensory changes to the ring and little finger, intrinsic muscle weakness and a positive tinel's .Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome is a compressive neuropathy of the ulnar nerve at the . Cubital tunnel syndrome happens when that nerve is irritated or compressed. A compressed ulnar can cause various uncomfortable and severe symptoms that, if left . The elbow flexion test for cubital tunnel syndrome draws the aponeurosis of the flexor carpi ulnaris taught over the ulnar nerve which may elicit symptoms of.
positive tinel's sign foot
positive tinel's sign
Ulnar nerve compression at the elbow is called cubital tunnel syndrome. Numbness and tingling in the pinky and ring fingers are common symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome. In most cases, symptoms can be managed with .Elbow flexion test as the sensitive of (0.32) provocative test in the diagnosis of cubital tunnel syndrome when combined with pressure on the ulnar nerve.
This test measures how fast signals travel down a nerve to find a compression or constriction of the nerve. Electromyogram. This test checks nerve and muscle function and may be used to .
Cubital tunnel syndrome is neuropathy of the ulnar nerve causing symptoms of numbness and shooting pain along the medial aspect of the forearm, also including the medial .
CuTS can be diagnosed by physical exam using Tinel’s sign, flexion-compression tests, palpating the ulnar nerve for thickening presence of local tenderness .Cubital tunnel syndrome is compression or traction of the ulnar nerve at the elbow. Symptoms include elbow pain and paresthesias in the ulnar nerve distribution. Diagnosis is suggested by .Ulnar nerve entrapment occurs when the ulnar nerve is compressed. This typically occurs at two main sites: the elbow and the wrist.Ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow is usually at the cubital tunnel (Cubital Tunnel .
Purpose: To determine the presence of cubital tunnel syndrome. Test Position: Standing. Performing the Test: The patient is standing and the examiner passively flexes the involved elbow to approximately 20 degrees. Next the .
Cubital tunnel syndrome: In cubital tunnel syndrome, damage to your ulnar nerve . If you experience symptoms of nerve compression or damage, a Tinel’s sign test can help your healthcare provider make a rapid diagnosis. You don’t need to live with numbness, pain or weakness. Talk to your healthcare provider about your symptoms, treatment .The Elbow Flexion Test is a neurological test to assess the presence of cubital tunnel syndrome, a common entrapment neuropathy. Skip to content . Clinical validity of the elbow flexion test for the diagnosis of ulnar nerve compression at the cubital tunnel. Acta orthopaedica belgica, 64, 366-370. Novak, C. B., Lee, G. W., Mackinnon, S. E . If the patient experiences a tingling sensation or electric shock-like feeling radiating down the forearm and into the hand, it may indicate nerve compression at the cubital tunnel. The elbow flexion test is performed by flexing the elbow and holding it in that position for a prolonged period, typically five minutes. What is cubital tunnel syndrome? Cubital tunnel syndrome is the most common type of ulnar nerve entrapment. The ulnar nerve runs along the medial (inside) of the arm and, when entrapped, can become irritated and cause pain or neuropathy. . resulting in ulnar nerve compression, or as a result of a previous trauma to the arm or elbow that .
Ulnar nerve entrapment occurs most commonly in the cubital tunnel or the ulnar tunnel, i.e., Guyon's canal. At the cubital tunnel, compression between Osborne's ligament, defined as the fascia connecting the two heads of the FCU superficially and the MCL of the elbow deep, can lead to symptoms of compressive neuropathy in the forearm and hand. Other potential points of compression near the elbow include the arcade of Struthers, against the medial humeral epicondyle just proximal to the cubital tunnel, and between the humeral and ulnar heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris distal to the cubital tunnel. Etiology. Specific causes of nerve compression at the cubital tunnel include: overuseCubital Tunnel Syndrome is compression or irritation of the ulnar nerve within a tunnel on the inside of the elbow behind a bone called the medial epicondyle (where your ‘funny bone’ is). . Other medical conditions may need to be evaluated such as thyroid disease or diabetes. A test called electromyography (EMG) and/or nerve conduction .
positive tinel sign at elbow
The 'Scratch Collapse Test' (SCT) has emerged as a new provocative test to assist in the localisation of peripheral nerve compression. The SCT is a diagnostic test for carpal tunnel syndrome and cubital tunnel syndrome. Technique [edit | edit source] Step 1. Patient position in standing or sitting. Step 2.
Cubital tunnel syndrome happens when the ulnar nerve, which passes through the inside of the elbow, is injured and becomes inflamed, swollen, and irritated. . Nerve conduction test. This test measures how fast signals travel down a nerve to find a compression or constriction of the nerve. Electromyogram. This test checks nerve and muscle . Cubital tunnel syndrome is rarer by a factor of 13, and the other compression syndromes are rarer still. Methods This review is based on publications retrieved by a selective literature search of PubMed and the Cochrane Library, along with current guidelines and the authors’ clinical and scientific experience.
The ulnar nerve is fairly flexible and can temporarily stretch up to 5mm, but sustained traction or compression may exceed the nerves resiliency, leading to symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome (2). . The “Elbow flexion test” is the best diagnostic maneuver for identifying cubital tunnel (6,7,8). The test entails maintaining shoulder .
Cubital tunnel syndrome is caused by entrapment or compression at the elbow. . But this test along with flexion-compression tests often don't provide enough evidence to diagnose the condition. A provider may recommend additional testing to confirm a diagnosis of ulnar nerve entrapment, such as: Cubital Tunnel Syndrome . carpal tunnel compression test (Durkan's test) is the most sensitive test to diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome. . less sensitive than Durkan compression test. Tinel's test. provocative . However, the most common area of compression is within the cubital tunnel in the elbow. The cubital tunnel lies beneath the Osborne ligament and is the passageway between the olecranon and medial .The research was done in 2016 to find a more suitable diagnostic test for carpal tunnel syndrome among carpal compression test (CCT), Tinel’s test (TT), and Phalen’s test (PT). The study shows sensitivity and specificity of the Carpal compression test were higher than both Tinel's and Phalen's tests.
Cubital tunnel syndrome is compression or irritation of the ulnar nerve in a tunnel on the inside of the elbow (where your 'funny bone' is). The ulnar nerve provides sensation to the little finger and part of the ring finger, and power to the small muscles within the hand. Carpal tunnel syndrome is the most common with a prevalence of 3% in the general population (15% in the workforce). 1 Cubital tunnel syndrome is also relatively common, with one U.S. metropolitan .We evaluated the elbow flexion test in 216 elbows without compression of the ulnar nerve at the cubital tunnel and without other neuropathies. We used Rayan's four positions as our test. The percentage of positive tests was only 3.6% at one minute, whereas evaluating the responses at three minutes w . Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most common peripheral mononeuropathy in the upper extremity. However, the diagnosis and treatment of cubital tunnel syndrome remains controversial without a standard algorithm. . . 1 Novak et al 25 previously reported higher sensitivity of elbow flexion compression test (91%) compared with Tinel sign .
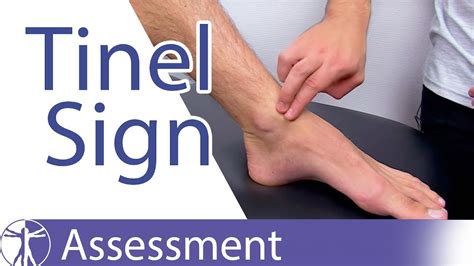
Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most common nerve compression occurring in the arm. . The ulnar nerve can be pinched at any point along its length, but the most common site of compression is on the cubital tunnel. . which gently stretches the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist through the extensor tunnel. Pain during this test is .Cubital tunnel syndrome is when your ulnar nerve gets compressed (squeezed) or irritated within the tunnel found on the inside of your elbow (where your ‘funny bone’ is). This compression or irritation stops the nerve from working correctly. Ulnar nerve compression Diagram showing where the ulnar nerve can be compressed on the inside of the .Purpose [edit | edit source]. Tinel's test is used to test for compression neuropathy, commonly in diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome.. Technique [edit | edit source]. It is performed by lightly tapping (percussing) over the nerve to elicit a sensation of tingling or "pins and needles" in the distribution of the nerve. The Tinel sign is the tingling or prickling sensation elicited by the . The objective of this study is to demonstrate the utility of the scratch collapse test (SCT) in localizing the point of maximal compression in cubital tunnel syndrome. From January 1, 2004 to December 1, 2005, 64 adult patients with cubital tunnel syndrome were evaluated by a single surgeon.
Several provocative maneuvers remain the core of the physical examination and allow distinguishing Cubital tunnel syndrome from other sites of nerve compression (i.e. C8 radiculopathy) [] (Table 11.1).A Tinel’s test, direct compression test, or placement of the elbow in a position of hyperflexion test (i.e. elbow flexion test) may all reproduce the patient’s symptoms.Even if the test is negative, you may still be having cubital tunnel syndrome. The test however can give an indication about the severity of the condition and also diagnose other conditions which may be confused with this. . In cases of advanced compression, the nerve may not recover fully even after release and in those cases, surgery .
22 de jul. de 2022 · Treasure Bowl is a slot inspired by the Orient as you’ll see when you’re playing it. The slot comes with a standard grid made up of 5 reels and 3 rows. But instead of the low number of ways to win, it comes with 243 ways to win. The symbols will fit the theme as is the case with most slot titles and they will come with all sorts of prizes.
cubital tunnel compression test|positive tinel's sign foot